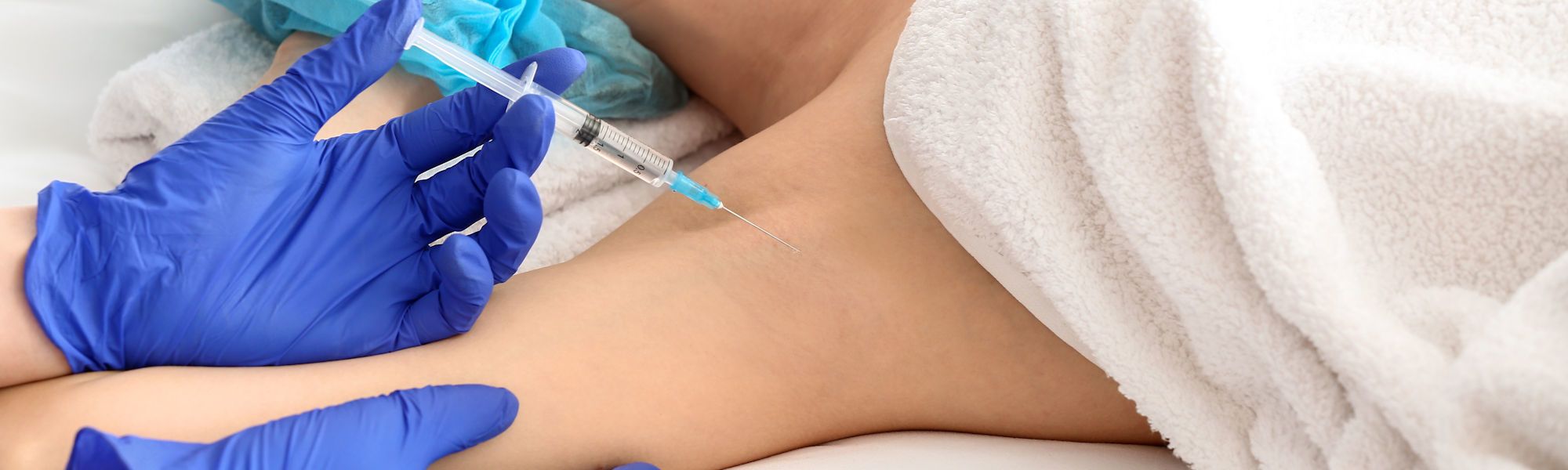
Originally, this therapy is used in neurology/psychiatry to treat muscle spasms. Botulinum toxin is a neurotoxin that stops the secretion of sweat. Sweat glands receive a nerve impulse to secrete their secretion. This nerve impulse is transmitted via the transmitter - or messenger - acetylcholine. The bacterial toxin Botox irreversibly blocks this transmitter, thus temporarily inhibiting sweat secretion.
In most cases, sweat secretion does not resume until months to a year later. Botox therapy is therefore not a permanent procedure for the treatment of hyperhidrosis. Botox is administered by adjusted doses in the form of skin injections. The skin areas affected by sweating are punctured. The number depends on the type of skin area as well as the intensity of sweating. Botox therapy does not cause any side effects.
However, there is a part of the population that is immune to this bacterial toxin (bia about 10%), so that in this case there is no effect of inhibition of sweating at all.